Master of Science in Life Sciences - Applied Computational Life Sciences
Life Scientist or Data Scientist? With us, you combine both!
AI, algorithms, and digital twins are transforming the life sciences. Those who master these disciplines stay one step ahead in the job market. Develop THE innovations that will shape a better future - together with our research groups and in collaboration with leading industry partners.


Why pursue a Master’s degree in Applied Computational Life Sciences?
Society, health, environment, and nutrition – these are the areas we focus on in the life sciences. As global challenges grow, so do the hopes and expectations for innovation within the life sciences. To meet these demands, life scientists must be agile, forward-thinking, and creative – and this is achievable through expanded skills in artificial intelligence and computational science.
From early detection of strokes through digital twins and computer-aided drug development to ecosystem modelling for nature conservation measures – such advancements are driven by computational life sciences.
In our Master’s programme, you’ll broaden your skills and build a bridge to the world of data. You can apply what you’ve learned immediately in practical projects, becoming part of a research group and collaborating with our industry partners.
This hands-on experience provides you with the ideal preparation for diverse career opportunities.
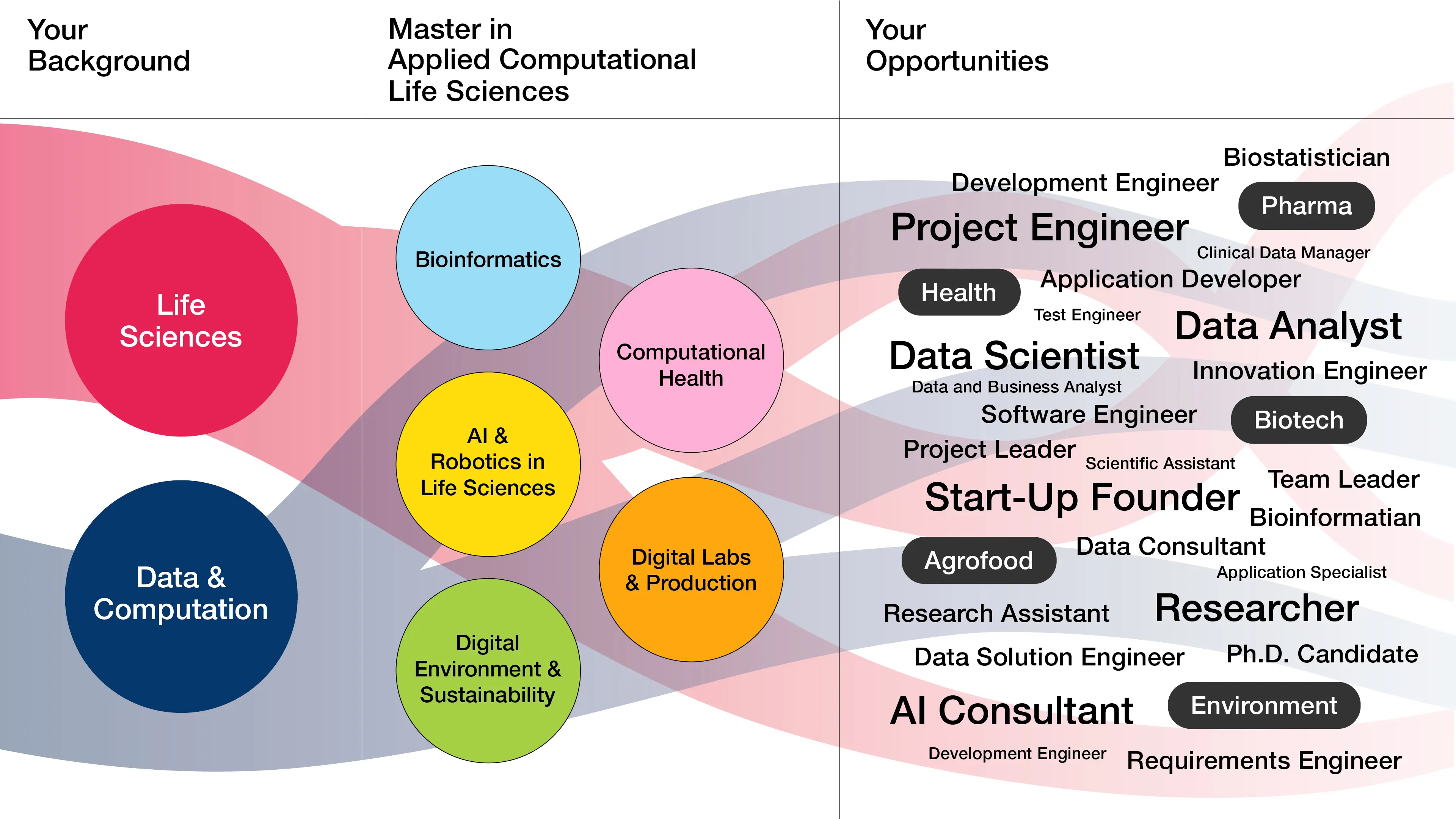
Deepen your knowledge in one of these 5 tracks
Computational Health
Use data- and model-based methods for addressing medical challenges. You will leverage machine learning on diverse medical data to uncover causal relationships. In doing so, you’ll employ technologies such as wearables and biosensors, discover digital biomarkers, and create tangible digital health solutions.
Bioinformatics
Work at the intersection of biology, medicine, and computer science. In this track, you’ll engage with the modelling of molecular biological processes, multi-omics approaches for biomarker discovery, the study of genomic evolution and adaptive changes, as well as the representation and integration of biomedical data.
Video portrait graduate: Moritz Kaufmann - From biotechnologist to PhD in Data Science
Digital Environment & Sustainability
Engage in sensor- and AI-based monitoring and modelling of natural systems and their interaction with humans. This includes questions related to smart farming and sustainability in a broader context, for example, concerning social and economic issues.
Digital Labs & Production
Connect people, spaces, and processes. In this track, you will focus on methodological and technological expertise in the digitalisation and virtualisation of labs, processes, and production facilities.
AI & Robotics in Life Sciences
Create new solutions based on a fundamental understanding of humans and machines as a unified learning system. In this track, you will focus on the application of deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and intelligent robotics in human interaction.
Your background
You have a bachelor’s degree in the life sciences or a related field. Other degrees may also be accepted. We are happy to advise you.

"At the University Hospital Zurich, a new data science project is initiated almost every week. For example, attempts are being made to use data analytics to gain new insights for the treatment of patients or to use AI models to calculate forecast probabilities for diagnoses. The solid understanding of data acquired during my studies helps me in my daily work with highly sensitive data, be it in the development of database interfaces or in the programming of various applications for data transformation and integration."
Matthias Joos, Graduate and Data Solution Engineer at the University Hospital Zurich
Career: What a Master’s degree in Life Sciences in Applied Computational Life Sciences will allow you to do.
The opportunities for graduates in this rapidly developing field of research and business are practically endless. Many find employment during their studies. They work as data analysts, data scientists, application developers or researchers in a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, agro-food, environment and medicine.
Suitable students have the opportunity to join our Data Science PhD programme, which is conducted in partnership with various Swiss universities.

Good reasons for a Master’s study in Wädenswil
- We offer a customisable Master’s programme which you can complete in 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7 semesters.
- The programme offers an attractive mix of modules from research, science, practice and business.
- You will have the opportunity to grow both as a professional and as a person, and to evolve into a sought-after specialist with leadership skills.
- We offer exciting research projects for your Master's thesis.
- You will be able to join a research group, where you can practice skills such as teamwork, initiative and critical thinking.
- You will benefit from small class sizes in the advanced modules, which offer interactive learning activities that will allow you to take charge.
Study programme and course content
Your studies include three areas of competence plus a Master's thesis, with a total of 90 credits (ETCS).
Based on your interests, before starting your studies you will work out your own personal learning objectives with your specialisation director and your supervisor. You will define the topic for your Master's thesis and design your own personal study path from the range of available modules.
Based on the topic of your Master's thesis, you will be assigned to a corresponding specialisation module that will fully prepare you for your Master's thesis. While working on your Master's thesis, you will be part of a research group that is working closely with our business partners or doing research at one of our institutes.
- Online study planner Your individual study plan.
- Master's thesis specialised fields Before starting your studies, you choose the field in which you want to write your research paper.
- Annual planning / timetables Important dates in the academic year.

"The Master's programme teaches you the skills you need for a digital future."
Dr. Matthias Nyfeler, specialisation director at the Institute of Computational Life Sciences
Your new skillset
- Processing and analysing data of various sizes and levels of complexity.
- Conceptual and technical skills to combine your expertise in a life sciences discipline with the potential of computational methods.
- Computational modelling and simulation of processes.
- Statistical modelling with machine learning and neural networks.
- Programming using modern scripting languages such as Python and R and you will understand the basic concepts of software and computer architectures.
- Analysis and solving of complex problems that combine scientific, social and entrepreneurial thinking.
- Planning, implementation, evaluation and presentation of major research and development projects.
Module overview
This module table is valid from 21. September 2025
Semester 1, ECTS: 30
Semester 2, ECTS: 30
3. Semester, ECTS: 30
Purple: Specialisation Modules / Green: Cluster Modules - you choose at least 9 ECTS / Blue: Core Competences - you choose at least 12 ECTS
The picture above shows the general structure of a full-time Master's programme. Students design their own study paths and choose their own focal points.
Together with your supervisor, you design your own individual study plan from the range of compulsory and elective modules. The selected modules are recorded in your individual study agreement (planning).
In addition, elective modules from the specialisations of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Chemistry for the Life Sciences or Food and Beverage Innovation can be taken.
Researching for practice
During your studies, you will expand your personal skills in technical expertise, and self-management. The practice-oriented research focus of your Master's thesis will foster your ability to innovate, change perspectives, and combine entrepreneurial with scientific thinking.
The work in your research group will not only help you develop your creativity, initiative and critical thinking abilities, but also your leadership and teamwork skills. We promote inductive, inquiry-based learning in small classes with interactive learning activities such as group work and presentations.
Theses
Interesting research questions are created with partners from industry and retail. Our graduates have already developed interesting, relevant and viable answers and solutions in their work.
Ready for the next step?
Do you have any questions?
This might also interest you
MSLS Community Centre
The Moodle learning platform for modules taught jointly with other universities of applied sciences!
Registration Master's programme
Organise your studies
MSLS Community Centre
Ready for a new chapter in your life? Apply now.
Fees, important dates, timetables and the Study App at a glance.
The Moodle learning platform for modules taught jointly with other universities of applied sciences!