Circular Economy
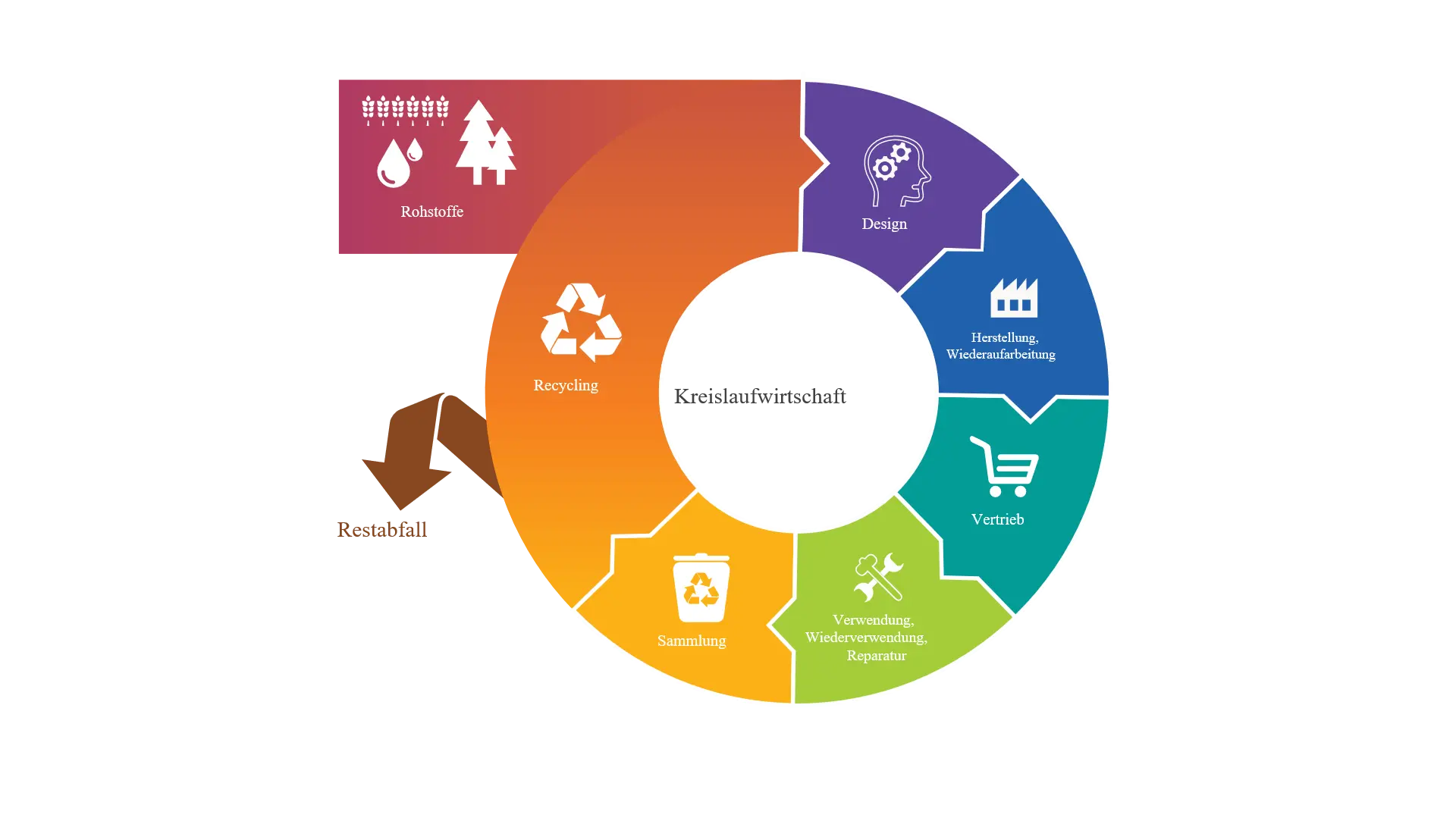
Function: Closed-loop economy - often also called or understood as Circular Economy, Cradle-to-Cradle-Economy or Upcycling - describes an economic system in which raw materials are used in closed cycles as far as possible. Waste products are considered from the outset as secondary raw materials in the process of planning, production, use and recycling. Construction, planning, maintenance, repair, reuse, reconditioning and recycling are designed as a holistic life cycle. Recycling plays a central role in this. Recycling management is the opposite of the linear economy with so-called "take-make-waste" models.
Advantages: Reduction of emissions, use of resources, energy requirements and waste. Potential business areas for industrial symbioses and product innovations (e.g. cement and gypsum from fly ash from power plants, terrazzo panels from construction waste)
Examples:
Initiatives: Circular Economy Switzerland; Product: Rental toilet "Kompotoi" generates fertilizer from human excrements. (Consulting: EPEA Switzerland)
Industrial symbiosis: Kalundborg/DK; recycling network from energy production and its waste materials together with pharmaceuticals, food industry, fertilizer production and other companies from various sectors.