Design Thinking
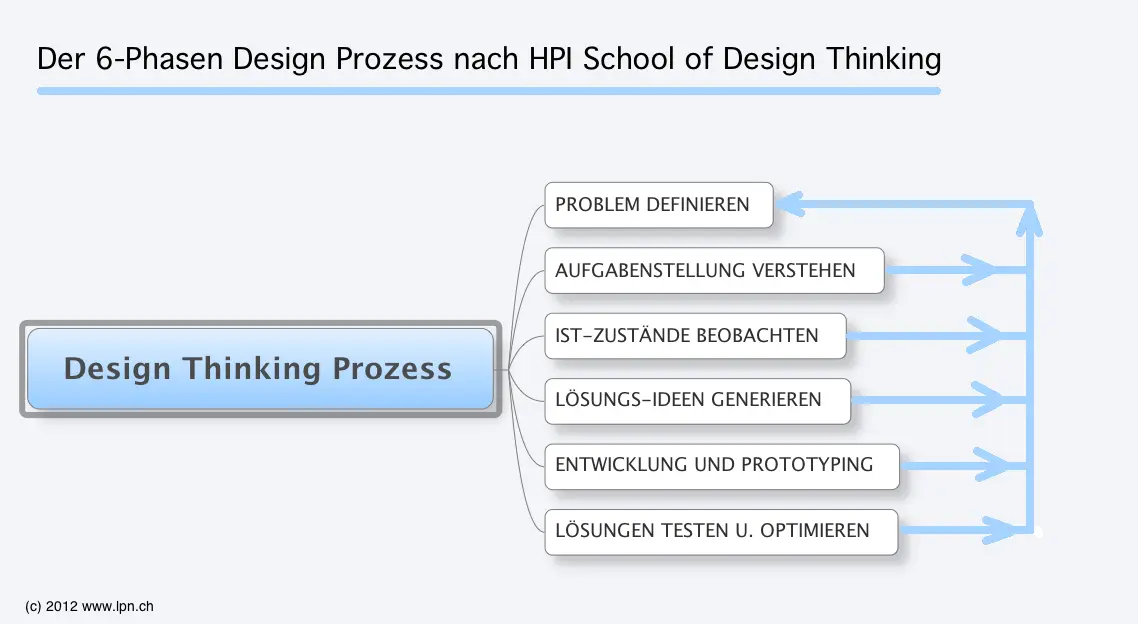
Background: Method from creative product development. The human being is at the centre of attention, the range of applications is unlimited. Goal: The goal is to think creatively, non-linearly, iteratively and interactively in order to arrive at concrete solutions in cooperation with the "target group".
Approach: In the run-up to the workshop, participants are given a general advice on the state of mind in Design Thinking: understand, observe and analyse, visualise, evaluate and optimise, implement. With this mindset, innovators (workshop participants, founders, department heads, employees) etc. can move through six phases from idea generation to implementation (see Figure). Characteristic for Design Thinking is the interaction with and observation of people. This ensures that the problem to be defined is also relevant for a future user. In phase 1, the problem definition, a field is defined in which a solution should/must be generated. This does not happen in empty space but is based on so-called explorative interviews and observations in the "market" or the natural environment. This first problem definition is deepened and tested in further discussions with "the target group" in phases 2 and 3 until the problem is understood to such an extent that concrete solutions can be generated in phase 4. In this phase it is helpful to use further methods of idea generation (see below) to arrive at concrete solution ideas, from which a prototype is developed in phase 5. This happens in phase 4 as well as in phase 5 again in close collaboration with the target group, through interviews, or rounds of presentations or open discussion. Important: the aim is not to discard an idea for a solution once it has been deemed good, but to refine the idea and prototype and bring them to the point where they are ready for use. This process is concluded in phase 6, in which the solution is presented to a wider public. At the same time, however, the development process is only complete when the obstacles (often referred to as teething troubles) that arose in phase 6 have been removed.
Advantage: The method is a combination of many methods and feedback loops. Problem definition, solution definition and solution design are developed in parallel and ensure relevance and user-friendliness. Offers again and again starting points for pragmatic as well as visionary ideas and solution concepts.
Disadvantage: Requires a high commitment from the team for a problem definition, time, and sociability. Phases 1-3 are very interactive and require experience in conducting interviews. In inexperienced and very diverse teams, experienced moderator necessary.
Further link: https://innovators-guide.ch/2013/02/design-thinking-2/